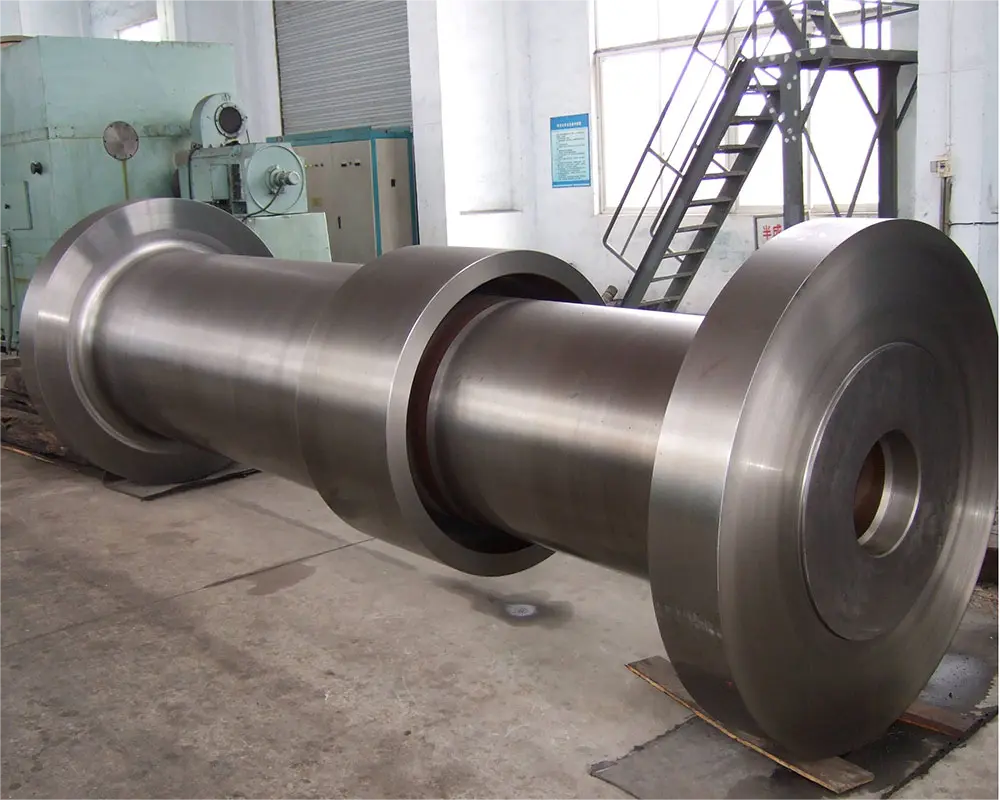
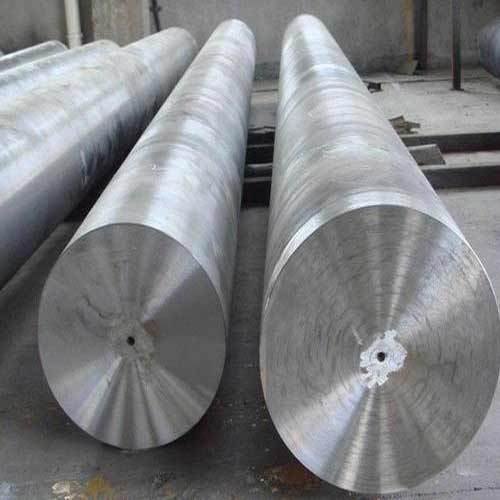
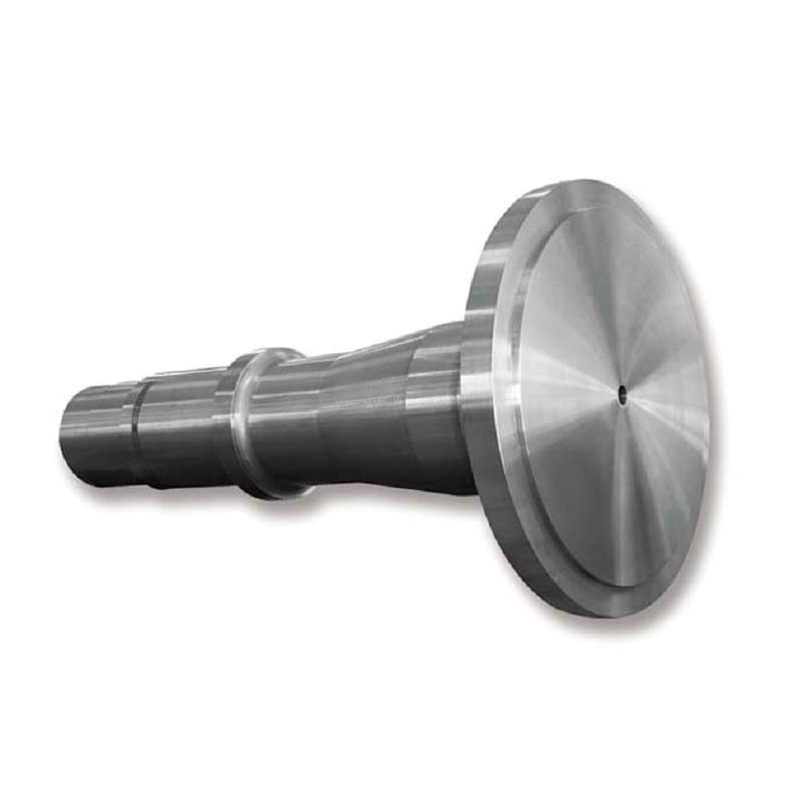
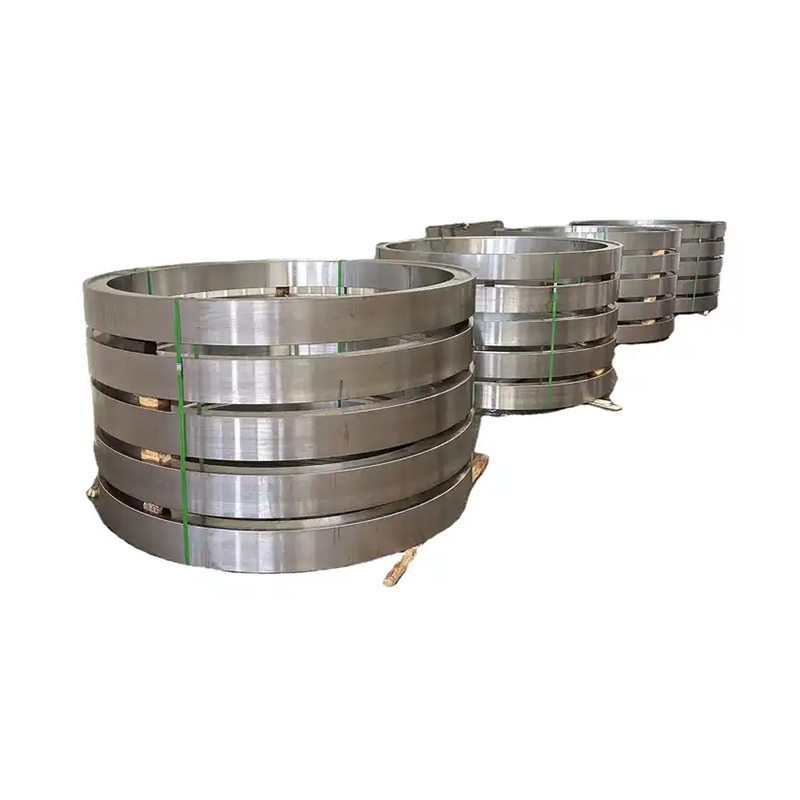
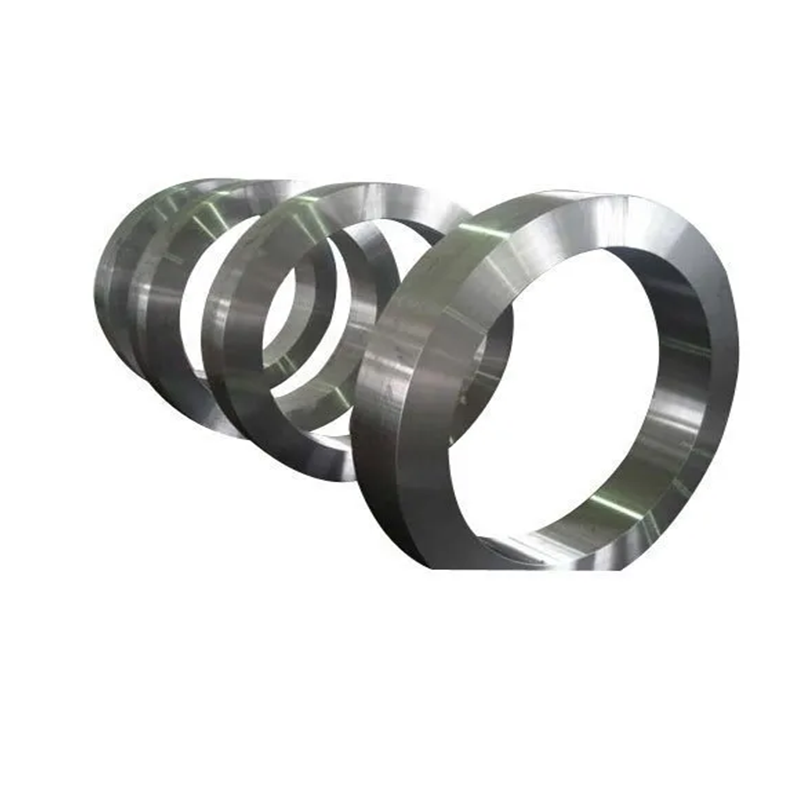
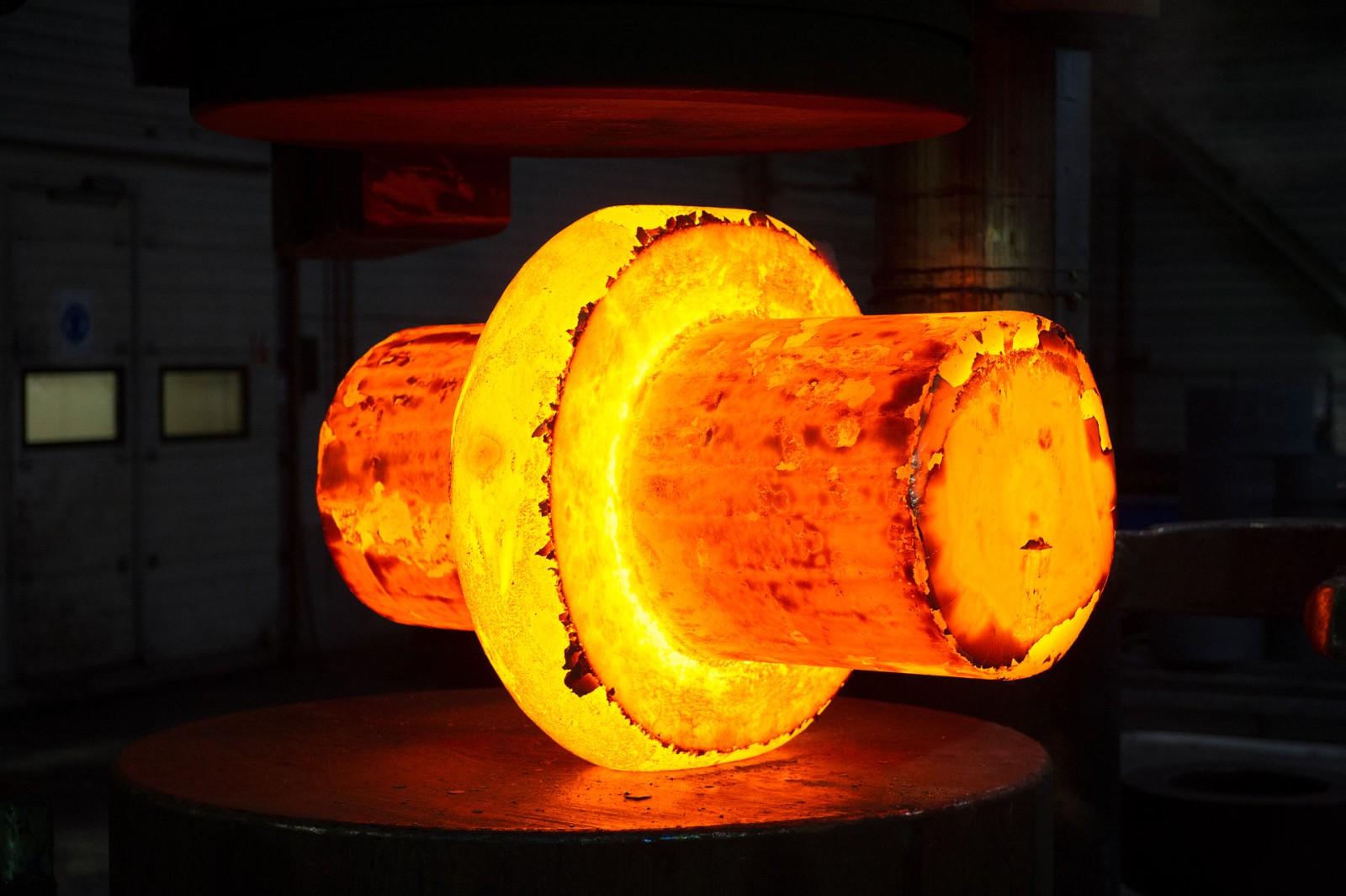
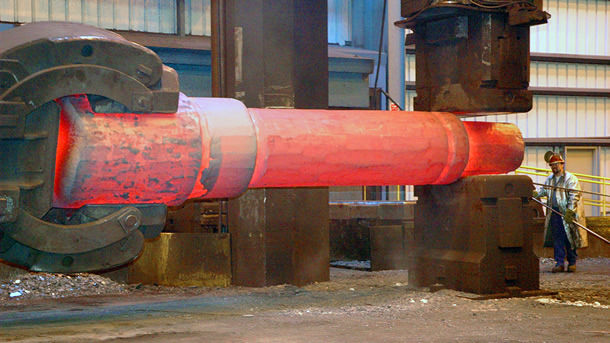
Experienced factory customization of large non-standard forged shaft high quality forgings parts
- LYHGB
- LUOYANG,CHINA
- 45 DAYS
- 4000 SETS/ MONTH
1.Forging refers to a workpiece or blank obtained by forging and deforming a metal billet.
Forging can use pressure on metal billets to cause plastic deformation and alter their mechanical properties. Forging can eliminate metal porosity. Holes improve the mechanical properties of forgings. Forgings have the following uses:
① General industrial forgings refer to civil industries such as machine tool manufacturing, agricultural machinery, agricultural tool manufacturing, and bearing industry.
② Forgings for hydroelectric generators, such as main shafts and intermediate shafts.
③ Forgings used in thermal power plants, such as rotors, impellers, retaining ring spindles, etc.
④ Metallurgical machinery, such as cold rolling rolls, hot rolling rolls, and herringbone gear shafts.
⑤ Forgings for pressure vessels, such as cylinder bodies, kettle ring flanges, and heads.
⑥ Shipboard forgings, such as crankshafts, tail shafts, steering rods, thrust shafts, and intermediate shafts.
⑦ Forging machinery equipment, such as hammer heads, hammer rods, hydraulic press columns, cylinder bodies, wheel axle press columns, and cylinder bodies, etc
2.Our company has many years of manufacturing and production experience, a professional technical team and complete machinery and equipment, as well as a professional after-sales business line, one-on-one service, and quality assurance. We have cooperated with many new and old customers both domestically and internationally multiple times. Please trust us and welcome you to inquire
Product detial
1.Forging refers to a workpiece or blank obtained by forging and deforming a metal billet.
Forging can use pressure on metal billets to cause plastic deformation and alter their mechanical properties. Forging can eliminate metal porosity. Holes improve the mechanical properties of forgings. Forgings have the following uses:
① General industrial forgings refer to civil industries such as machine tool manufacturing, agricultural machinery, agricultural tool manufacturing, and bearing industry.
② Forgings for hydroelectric generators, such as main shafts and intermediate shafts.
③ Forgings used in thermal power plants, such as rotors, impellers, retaining ring spindles, etc.
④ Metallurgical machinery, such as cold rolling rolls, hot rolling rolls, and herringbone gear shafts.
⑤ Forgings for pressure vessels, such as cylinder bodies, kettle ring flanges, and heads.
⑥ Shipboard forgings, such as crankshafts, tail shafts, steering rods, thrust shafts, and intermediate shafts.
⑦ Forging machinery equipment, such as hammer heads, hammer rods, hydraulic press columns, cylinder bodies, wheel axle press columns, and cylinder bodies, etc
2.Characteristics of Forgings
1) Large weight range. Forgings can range from a few grams to several hundred tons
2) Higher quality than castings. The mechanical properties of forgings are better than those of castings, and they can withstand large impact forces and other heavy loads. Therefore, forgings are used for all important and heavily stressed parts.
For high carbide steel, forgings have better quality than rolled materials. High speed steel rolling materials can only meet the usage requirements after being modified and forged. Especially high-speed steel milling cutters must be forged.
3) The heaviest is the lightest. On the premise of ensuring design strength, forgings are lighter than castings, which reduces the weight of the machine itself and is of great significance for transportation vehicles, airplanes, vehicles, and aerospace equipment.
4) Save raw materials. For example, for a crankshaft with a static weight of 17kg used in automobiles, when using rolled material for cutting and forging, the chips account for 189% of the crankshaft weight, while when using die forging, the chips only account for 30%, which also reduces machining time by 1/6.
Precision forged forgings not only save more raw materials, but also save more machining hours.
5) High productivity. For example, using two hot forging presses to forge radial thrust bearings can replace 30 automatic cutting machines. When using a top forging automatic machine to produce M24 nuts, the productivity of a six axis automatic lathe is 17.5 times higher.
6) Free forging has great flexibility, therefore, forging methods are widely used in some repair factories to produce various accessories.

Product display